Customize your BibTeX output
You can customize how Paperpile generates BibTeX output so your BibTeX entries match the exact specifications needed for your LaTeX documents. These settings control the format and content of exported files, copied citations, and automatically synced bibliography files.
Choose between classical BibTeX format and the more modern BibLaTeX format, the fields you want to include in your BibTeX export, and more.
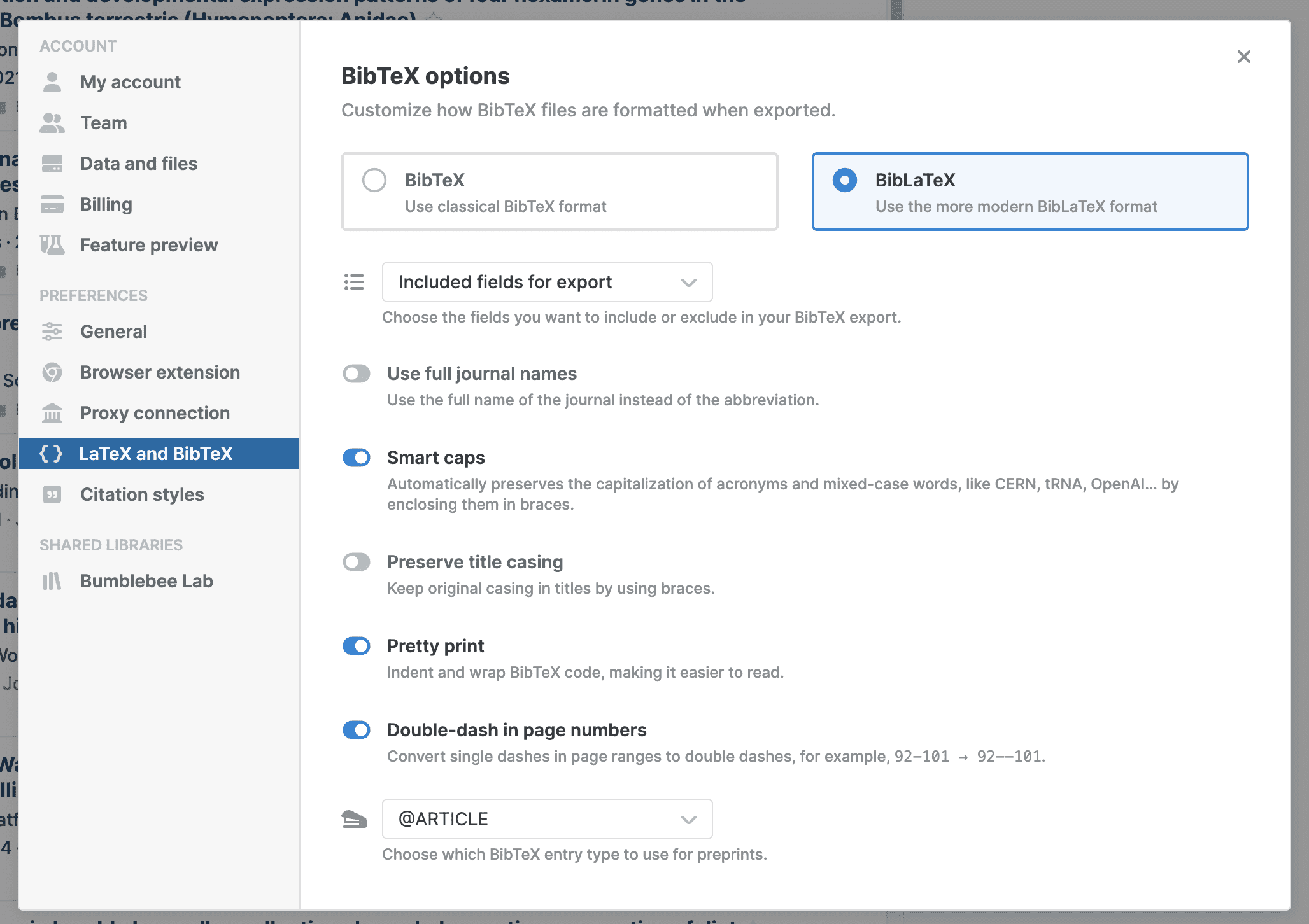
Click your profile picture in the top right and go to Settings > LaTeX and BibTeX to view options for BibTeX and BibLaTeX output:
The settings you select will apply to
- Exported files: Bibliography files you download from Paperpile. See Export BibTeX files.
- Copy and paste: BibTeX entries and LaTeX commands you copy to the clipboard. See Copy and paste BibTeX and LaTeX commands.
- Automatically synced BibTeX files: Bibliography files are synced through Workflows and Integrations. See Automatically sync BibTeX files.
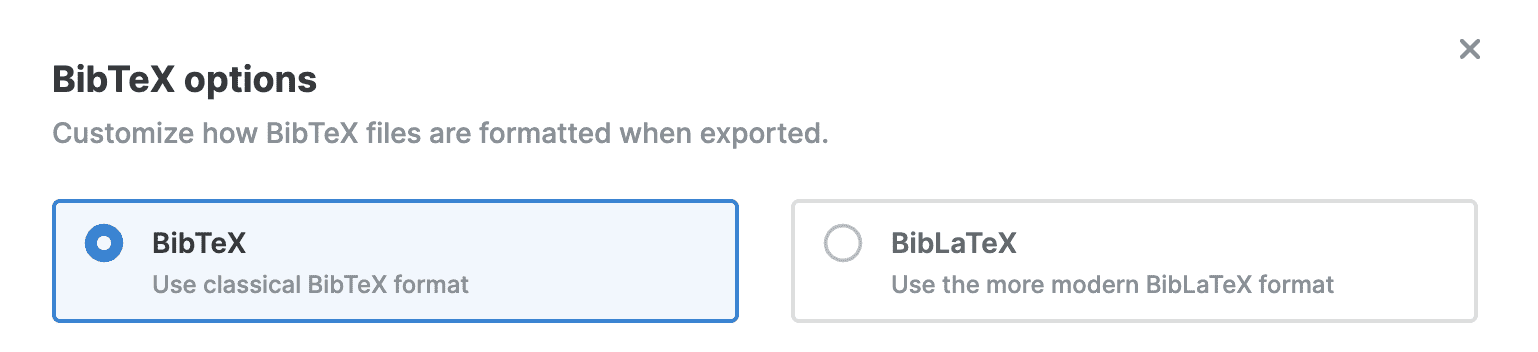
Choose between BibTeX and BibLaTeX
BibTeX is the traditional bibliography format that works with most LaTeX distributions and bibliography styles. BibLaTeX is a more modern alternative that offers additional features and better Unicode support.
Use BibTeX if:
- You're working with a journal or publisher that requires traditional BibTeX format.
- Your LaTeX template or document class specifically requires BibTeX (a bibliographic style file with .bst extension).
Use BibLaTeX if:
- You need better Unicode and international character support.
- You need more advanced bibliography features like footnotes.
BibTeX and BibLaTeX differences
BibTeX and BibLaTeX are two different bibliography systems for LaTeX:
- BibTeX format: The older format that works with the standard \bibliographystyle{} and \bibliography{} commands in LaTeX. It relies on external .bst files (bibliography style files) to format citations and bibliographies.
- BibLaTeX format: A newer system with extended features and different syntax that requires the BibLaTeX package in your LaTeX document.
Key differences between BibTeX and BibLaTeX include their level of control over citations and bibliographies:
- BibTeX does not natively support UTF-8 encoding in .bib files. Special characters (like é or ß) must be entered using LaTeX commands, such as \'{a} for á.
- BibLaTeX fully supports UTF-8 encoding—it is Unicode-aware and expects UTF-8 encoded .bib files. You can directly use UTF-8 characters without LaTeX commands. The default backend, biber, is designed to handle modern encoding standards.
- BibLaTeX combines bibliographic data management with flexible citation and bibliography formatting. It supports advanced features like multiple bibliographies, footnote citations, and multiple languages without requiring external files.
- BibLaTeX supports a greater number of BibTeX fields and reference types than BibTeX.
- A key difference between BibTeX and BibLaTeX is how publication dates are handled.
- In BibTeX, month and year are separate fields:
@article{example, author = "Author, A.", title = "Title of the Article", journal = "Journal Name", year = 2024, month = jan } - BibLaTeX uses ISO 8601 format for dates (YYYY-MM-DD). It combines year, month, and optionally day into a single date field:
@article{example, author = {Author, A.}, title = {Title of the Article}, journal = {Journal Name}, date = {2024-01-15} }
- In BibTeX, month and year are separate fields:
While BibLaTeX is more modern, BibTeX remains widely used for its simplicity and compatibility.
BibTeX output options
- Included fields for export: Select which BibTeX fields to include in your BibTeX output from the menu. You can choose to export all fields or only standard fields to keep your bibliography files clean and focused.
- Escape Unicode characters: Switch on to convert special UTF-8 characters, like accented letters, to LaTeX commands that work with older BibTeX processors. An option for BibTeX settings only since BibLaTeX automatically supports UTF-8 characters.
- Use full journal names: Switch on to export complete journal names instead of abbreviations. For example, you can choose to have PLOS Computational Biology, just like in the Journal (full title) Paperpile field, instead of the abbreviation PLOS Comput Biol used in the Paperpile Journal field. Turn this on if your citation style requires full journal names.
- Smart caps: Switch on to automatically protect capitalization in reference titles by adding braces around words that should stay capitalized (like proper nouns and acronyms). This prevents bibliography styles from changing the capitalization incorrectly.
- Preserve title casing: Switch on to keep the exact capitalization from your reference titles without any automatic modifications. Use this when you want complete control over how titles appear in your bibliography.
- Pretty print: Switch on to format the BibTeX output with indentation and line breaks to make it more readable when you open files in a text editor.
- Double-dash in page numbers: Switch on to convert page ranges like "123-456" to "123--456" using LaTeX's preferred double-dash format for proper typesetting of page ranges.
- Entry type for preprints: Choose the BibTeX entry type to use for preprints from a menu.

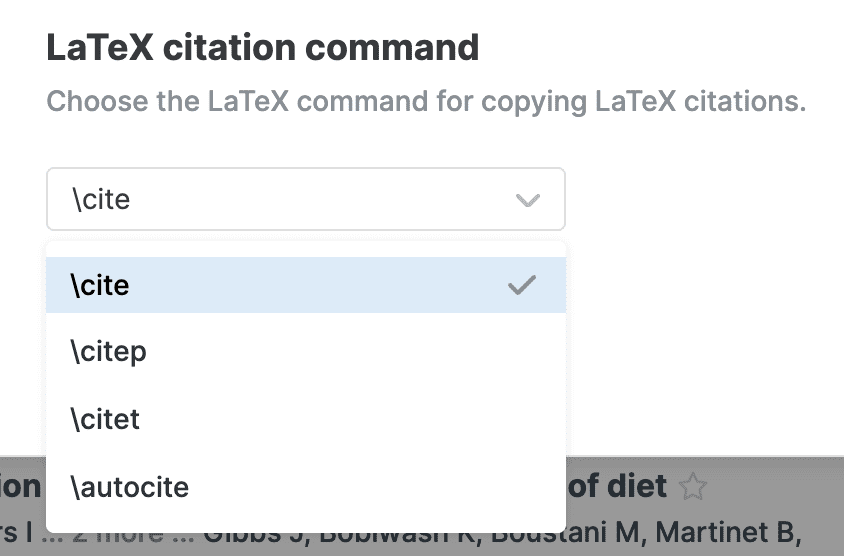
- LaTeX citation command: This setting controls which LaTeX command is used when you copy citations. Select your preferred citation command from the menu.
Customize BibTeX keys
You can customize the pattern for your BibTeX keys.
Go to Settings > General and click Set citation key pattern. See Citation keys.
Common questions
My BibTeX file won't compile in my LaTeX document. What's wrong?
This usually happens when there's a mismatch between the BibTeX output format and your LaTeX setup. If you're using traditional BibTeX in your LaTeX document, make sure you export in BibTeX format, not BibLaTeX format. The two formats have different syntax and aren't compatible with each other.
To check your export format in Paperpile: click your profile picture in the top left, go to Settings > LaTeX and BibTeX and look at which BibTeX output options you have selected. Choose BibTeX for traditional BibTeX workflows or BibLaTeX if you're using the BibLaTeX package in your LaTeX document.
My .bst file has problems with special characters (like é). What should I do?
Some .bst styles and BibTeX compilers are not Unicode-aware. Switch on the Escape Unicode characters toggle to convert UTF-8 to LaTeX commands (for example, é → \'{e} ). If you must keep UTF-8 characters, switch to BibLaTeX format, and use the BibLaTeX package and a BibLaTeX specific compiler like biber in your document.