Is Google Scholar an academic database?

According to major database providers, Google Scholar is sometimes considered a database and sometimes a search engine. While related services such as Web of Science, Scopus, or Medline all declare on their websites that their offered services are databases, Google Scholar does not do so, and that's the root of the confusion.
The core features of academic databases
1. Scope
Databases typically cover a certain scope. Google Scholar does not search the entire public web. It limits its scope to resources from academic publishers, universities, and academic repositories.
Scopus and Web of Science have an editorial team that manages a list of sources that are included in their database, while Google Scholar adds to its index anything that looks like an:
- academic article
- research report
- thesis
- working paper
- book chapter
It does so according to its built-in algorithm.
➡️ Visit out guide to the best academic databases.
2. Stable document identifier
A stable document identifier is a unique identifier for documents that facilitates retrieval across browsers and platforms. The most common type is a DOI, or digital object identifier.
A stable document identifier uniquely identifies a document. A single link, like a DOI, containing the identifier allows others to retrieve the same information as you. Major databases like Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed offer a stable document identifier, but Google Scholar does not.
Copying a Google Scholar result link into your browser’s toolbar does not necessarily yield the same result over time. This could be because your search results are influenced by your geographical location or your browsing history. Google Scholar adds thousands of new articles per day, which changes the search results.
➡️ Read more about what a DOI is.
3. No record should be removed
Another feature of academic databases is that documents once indexed are not removed. Because of how Google Scholar works, a single search result may not appear in future searches.
Google Scholar constantly not only crawls the web for new sources, but also checks existing ones. If Google Scholar finds that a document already indexed was removed from a university repository, and there is no other copy available on the web, it will also delete it from its own search index.
Google Scholar is an academic search engine
Based on these criteria, we conclude that Google Scholar is an academic search engine, rather than a database. Since it doesn’t use stable document identifiers, there’s no guarantee that the results you see in one search can be replicated exactly in the future.
➡️ Check out our guide on how to use Google scholar or visit our list of the best academic search engines.
Get the most out of Google Scholar
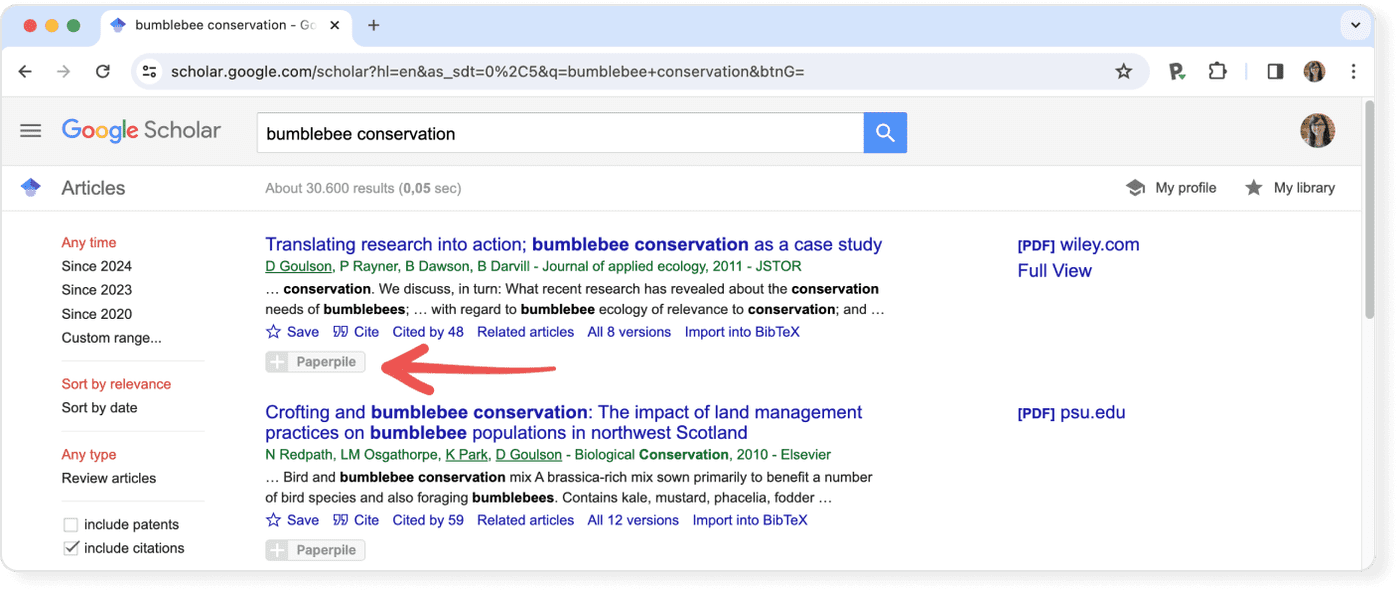
Use a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with Google Scholar and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and cite them in thousands of citation styles:
Frequently Asked Questions about Google Scholar
⚽ Is Google Scholar an academic source?
No. Google Scholar is an academic search engine, but the records found in Google Scholar are academic sources.
🎳 Is Google Scholar peer reviewed?
No. Google Scholar collects research papers from all over the web, including grey literature and non-peer reviewed papers and reports.
🏈 Are Google Scholar articles free?
Google Scholar does not provide any full-text content itself, but links to the full text article on the publisher page, which can either be open-access or paywalled content. Google Scholar, however, tries to provide links to free versions of the article, when possible.
🎾 What is the Google Scholar Button?
The Google Scholar Button is a browser extension that allows you to easily access Google Scholar from any web page. You can install it from the Chrome Webstore.


