The top list of research databases for medicine and healthcare

Web of Science and Scopus are interdisciplinary research databases and have a broad scope. For biomedical research, medicine, and healthcare there are a couple of outstanding academic databases that provide true value in your daily research.
Scholarly databases can help you find scientific articles, research papers, conference proceedings, reviews and much more. We have compiled a list of the top 5 research databases with a special focus on healthcare and medicine.
1. PubMed
PubMed is the number one source for medical and healthcare research. It is hosted by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and provides bibliographic information including abstracts and links to the full text publisher websites for more than 28 million articles.
- Coverage: around 35 million items
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✘
- Cited by: ✘
- Links to full text: ✔
- Export formats: XML, NBIB
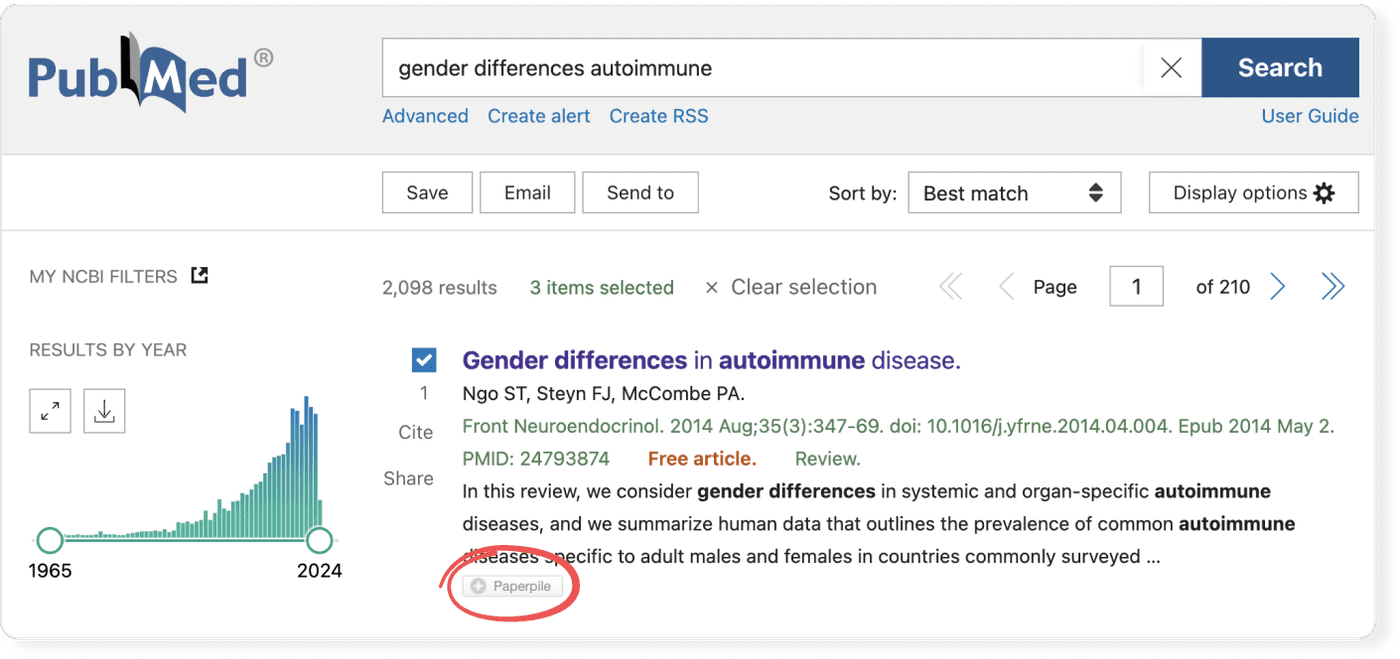
Pro tip: Use a reference manager like Paperpile to keep track of all your sources. Paperpile integrates with PubMed and many popular databases. You can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons and later cite them in thousands of citation styles:
2. EMBASE
EMBASE (Excerpta Medica Database) is a proprietary research database that also includes PubMed. It can also be accessed by other database providers such as Ovid.
- Coverage: 38 million articles
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Full text: ✔ (requires institutional subscription to EMBASE and individual publishers)
- Export formats: RIS

3. Cochrane Library
The Cochrane Library is best know for its systematic reviews. There are 53 review groups around the world that ensure that the published reviews are of high-quality and evidence based. Articles are updated over time to reflect new research.
- Coverage: several thousand high quality reviews
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✘
- Full text: ✔
- Export formats: RIS, BibTeX

4. PubMed Central (PMC)
PubMed Central is the free, open access branch of PubMed. It includes full-text versions for all indexed papers. You might also want to check out its sister site Europe PMC.
- Coverage: more than 8 million articles
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✔
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✔
- Full text: ✔
- Export formats: APA, MLA, AMA, RIS, NBIB

5. UpToDate
Like the Cochrane Library, UpToDate provides detailed reviews for clinical topics. Reviews are constantly updated to provide an up-to-date view.
- Coverage: several thousand articles from over 420 peer-reviewed journals
- Abstracts: ✔
- Related articles: ✘
- References: ✔
- Cited by: ✘
- Full text: ✔ (requires institutional subscription)
- Export formats: ✘
Frequently Asked Questions about research databases for medicine and healthcare
📗 What is PubMed?
PubMed is the number one source for medical and healthcare research. It is hosted at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and provides bibliographic information including abstracts and links to the full text publisher websites for more than 35 million items.
📕 What is EMBASE?
EMBASE (Excerpta Medica Database) is a proprietary research database that also includes in its corpus PubMed. It can also be accessed by other database providers such as Ovid.
📘 What is Cochrane Library?
The Cochrane Library is best know for its systematic reviews. There are 53 review groups around the world that ensure that the published reviews are of high-quality and evidence based. Articles are updated over time to reflect new research.
📙 What is PubMed Central (PMC)?
PubMed Central is the free, open access branch of PubMed. It includes full-text versions for all indexed papers. You might also want to check out its sister site Europe PMC.
📒 What is UpToDate?
Like the Cochrane Library, UpToDate provides detailed reviews for clinical topics. Reviews are constantly updated to provide an up-to-date view.


