How do you identify a scholarly source?
Are you unsure if your source is a scholarly source? This article provides you with six identifiers for scholarly sources.
1. Author
Is the author a scholar? Are the names and credentials of all authors provided? Also make sure to check if the author lists their affiliations (universities, hospitals, research institutions, think tanks, ...).

2. Publisher
Who is the publisher of the information? Is the journal publishing peer-reviewed articles? Is the date of publication evident? Either do a fact check on the website of the journal or publisher or check if the journal is indexed in bibliographic databases like PubMed, Web of Science, or Scopus.
3. Content
Who is the intended audience of the article? Check if the article is research-based and aims at creating new knowledge or if the purpose is merely to persuade, report, entertain, or inform the audience.
4. Language
Review the language and tone of the article. Is the language of the article formal, technical, and that of the discipline covered?
5. Structure
Does the article have an abstract or descriptive summary of its contents? How does the article look overall; does it have charts, graphs, and tables? Check if the article is well structured, if any research carried out is well documented, and if the conclusions are based on evidence.
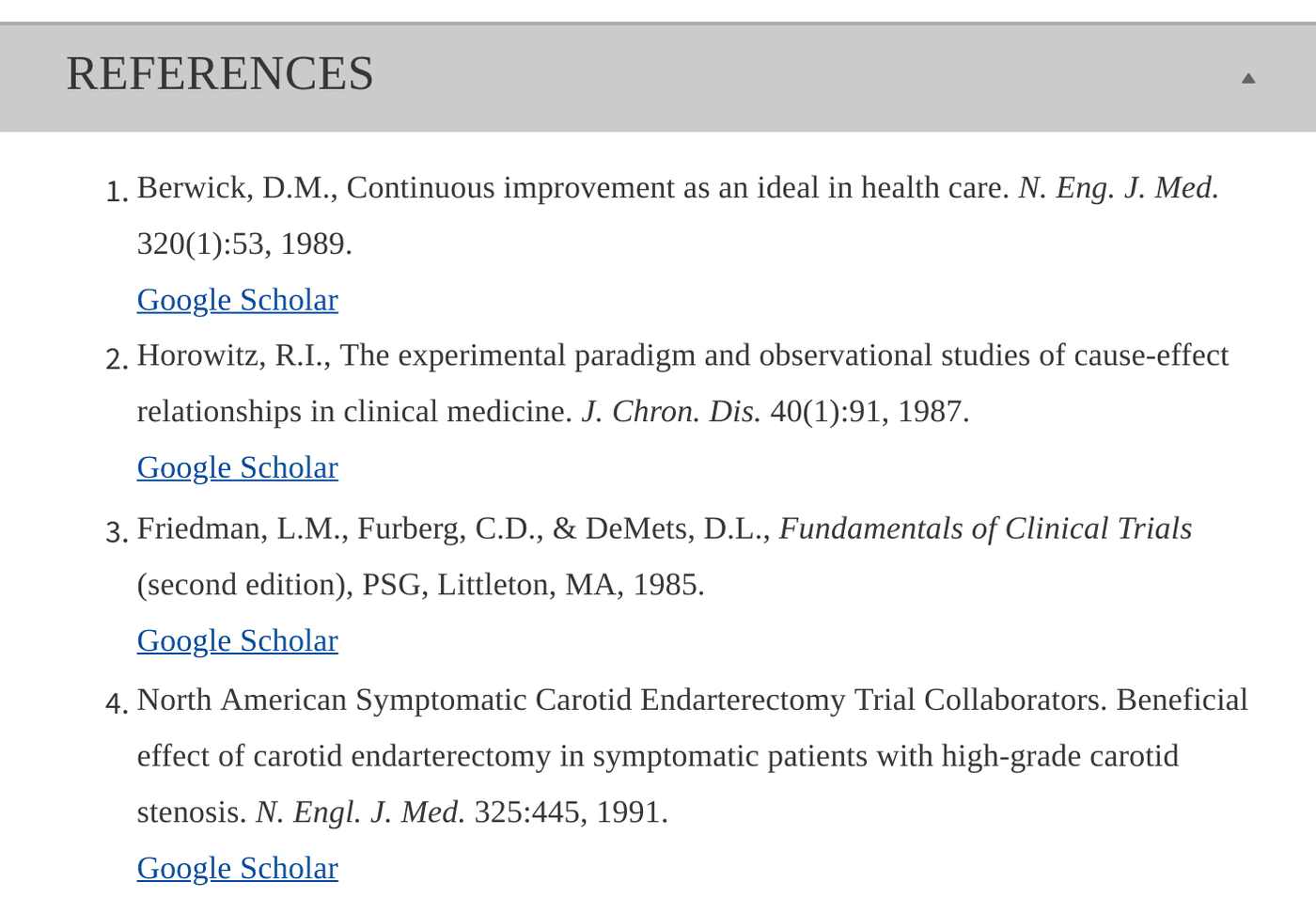
6. References
Are sources cited in the form of footnotes or bibliographies? Is there a reference list at the end of the article like in the example below?
Frequently Asked Questions about identifying scholarly sources
🥑 What is a scholarly source?
Scholarly sources (also called academic, peer-reviewed or refereed sources) are written by and for faculty, researchers, or scholars. We refer to scholarly sources here as scholarly, peer-reviewed journals, but they can be anything from books to conference publications, either electronic or print-based. These sources will provide the most substantial information for your research.
🥭 Which elements define a scholarly source?
Scholarly sources contain the following elements:
- The authors are scholars or researchers with known affiliations and credentials.
- The language used is academic and complex.
- The article contains full citations to other scholarly sources.
- Scholarly articles are often peer-reviewed by specialists.
- The publisher is a scholarly press with editorial reviews.
- The intended audience is other faculty, researchers, or scholars.
🍓 How is a non-scholarly source defined?
Non-scholarly sources are written by non-academics, and they can be primary sources, news sources, data and statistical publications, book reviews, or editorials.
🥔 Which elements define a non-scholarly source?
Non-scholarly sources are mostly written for a general audience, are often opinion based, written in non-technical language, are not peer-reviewed, and may lack references to other sources.
🍍 Can I use both scholarly and non-scholarly sources in my paper?
You can definitively use scholarly sources in your paper. As for non-scholarly sources, you probably can use them too. Make sure to check with your supervisor first if using non-scholarly sources is allowed.